Project Description
Shifting Folds is computational study to automatically identify the minim amount of linear actuators necessary to fold an origami. The end goal is to develop an algorithm that can autonomously place the motion actuators, map their positions to the open and closed states of the origami and control the overall shape of the folding element. Traditional and more complex origami patterns were used in order to test the feasibility of the system.
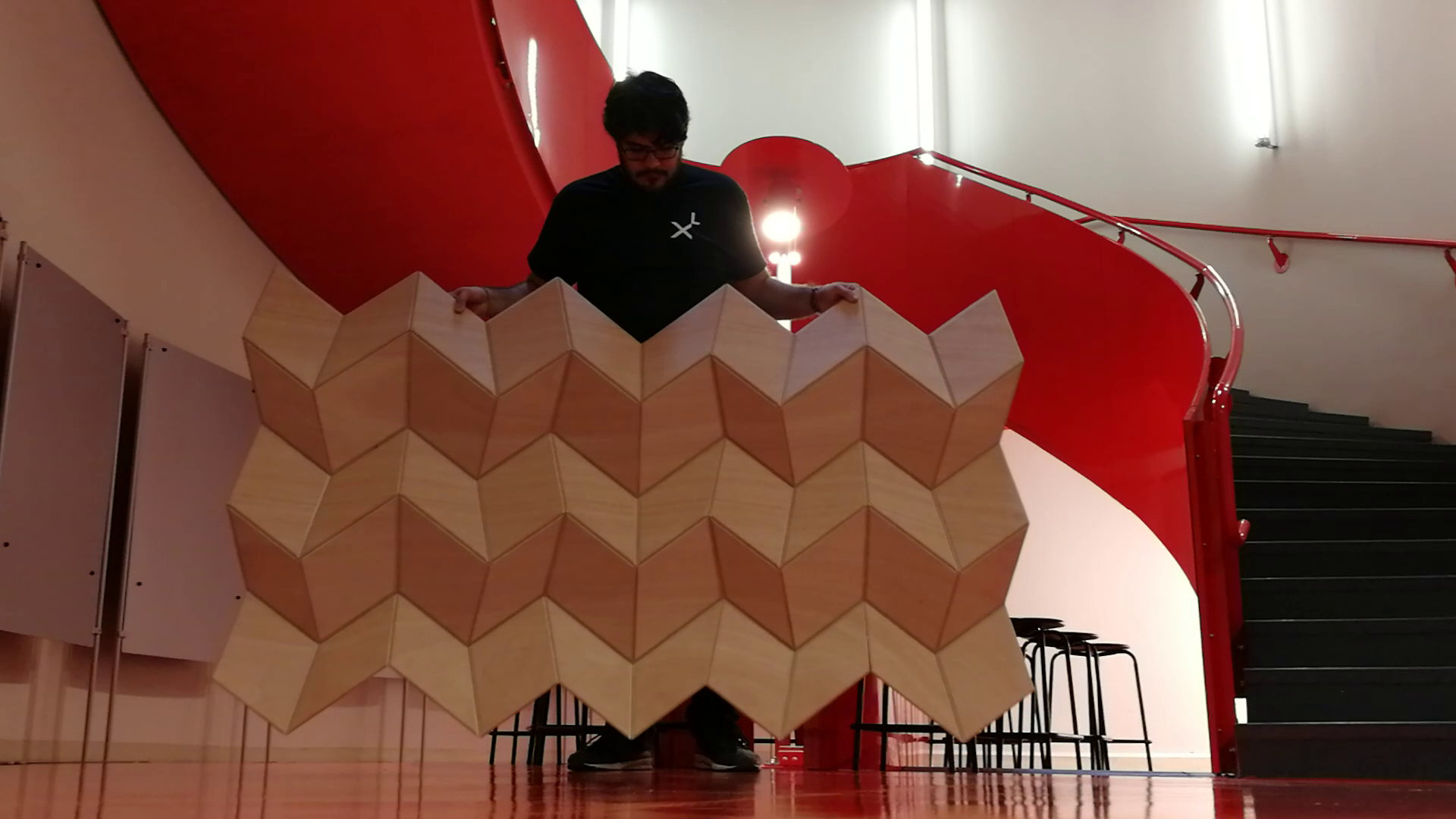

images courtesy of INDEXLAB
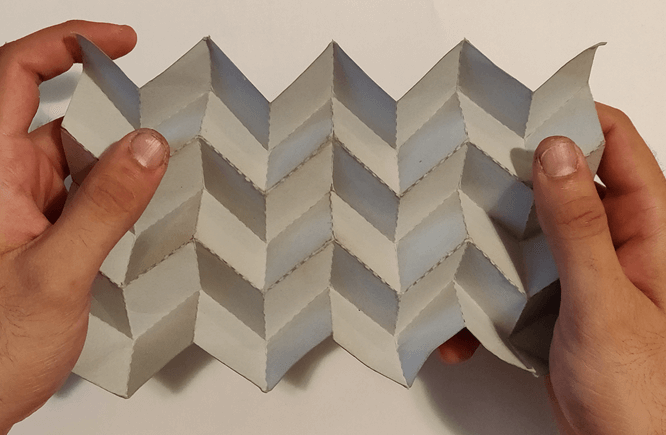
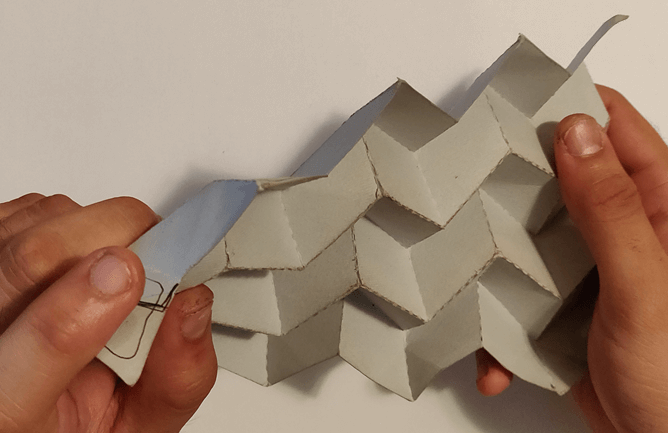
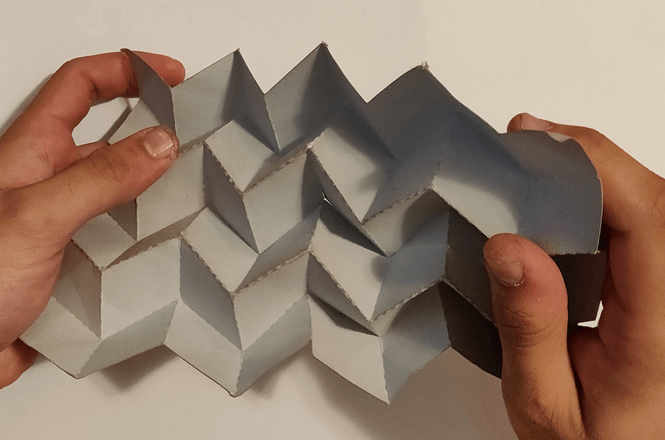
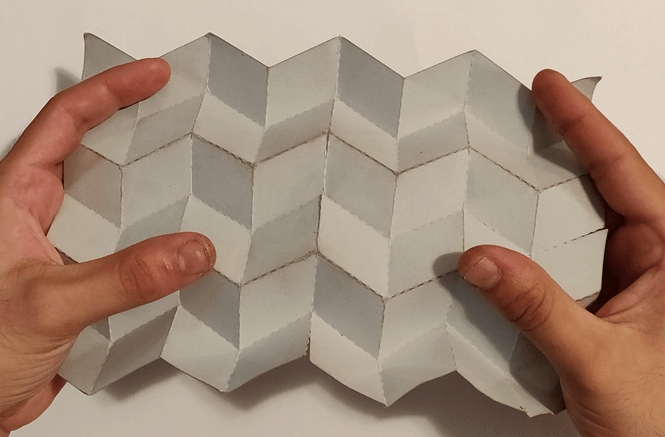
The Origami Fold
Given a origami pattern to analyze the proposed system evaluates its folding behavior, identifying the crease edges and their fold direction (mountain or valley folds). The first output is an unconstrained geometry, expanding and contracting above a 2D surface.
By selectively constraining opposing vertex pairs different motion configurations are evaluated. For each one the 3D paths of each vertex are computed and compared for complexity and compliance to the boundary conditions. Specifically, constraints are added to selected origami vertices, limiting their movement in the Z direction (bounding them to the 2D surface) and in the X directions.
Once the main constraints are imposed the overall motion of the origami is computed evaluating the expansion/contraction rate of each control point in 3D space. The constrained vertices represent ideal locations where to install motion systems for the origami system.
The Motion System
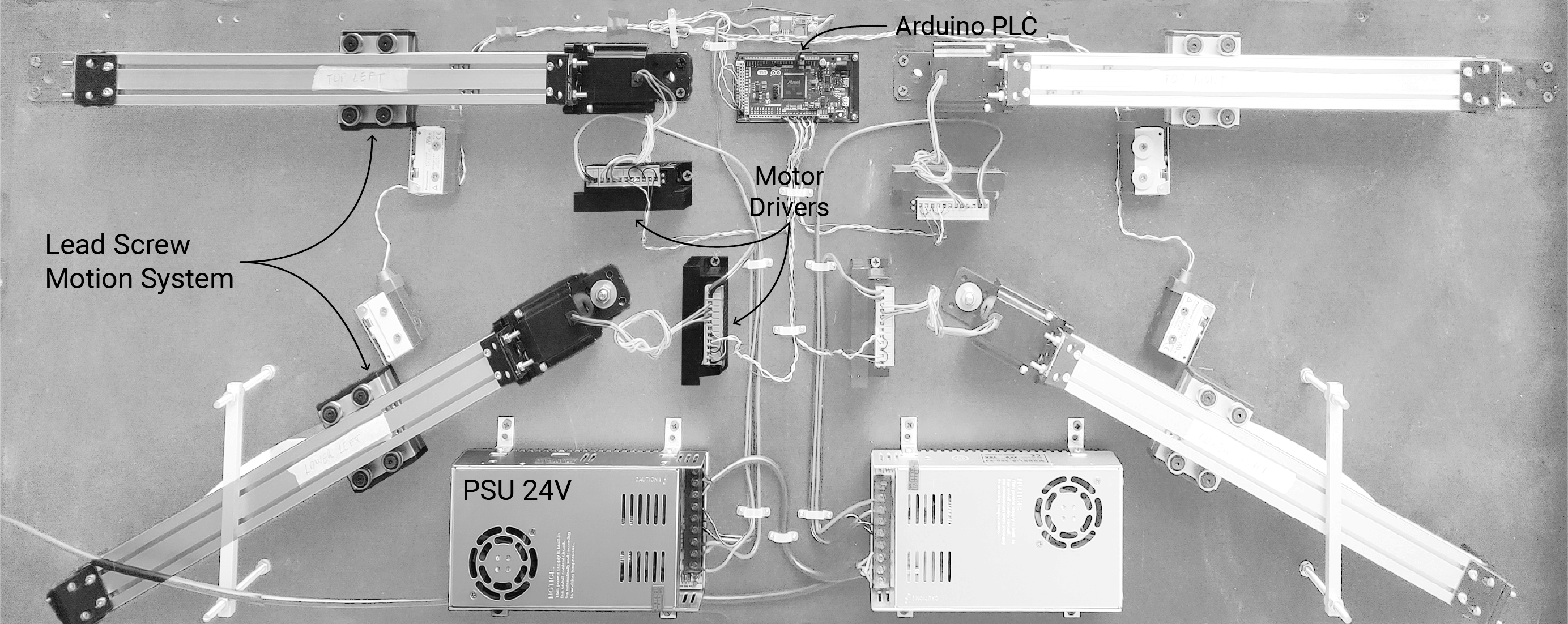
The motion system is compose of four linear actuators whose position is regulated from an Arduino PLC. The system relies on physical end-stops in to avoid drifting misalignments in the actuator movement. In case of power loss or reset, the actuator perform an homing procedure before accepting any inputs.
The Origami Panel
images courtesy of INDEXLAB
The adaptable shape of the origami panels makes them ideal for regulating the acoustics of rooms and environments. By integrating sensors the shape of the origami could be automatically adjusted based on external inputs.